Exploring the Differences and Synergies: CRM vs. CMS in Customer Management Systems

In a marketplace dominated by customer-centricity, the battle between CRM vs. CMS intensifies. Are you maximizing your understanding of customer relationships and content delivery?
As we unravel the distinctions and synergies, envision the potential for improved customer satisfaction, heightened engagement, and business growth through effective CRM and CMS integration.
Join us on this journey as we navigate the intricate dance between CRM vs. CMS, empowering your marketing strategies and propelling your business toward unparalleled success.
Content Overview:
Understanding CRM (Customer Relationship Management)
In the world of marketing, customer relationships are the lifeblood of any successful business. They’re the foundation for repeat business, positive word-of-mouth, and sustainable growth. But keeping track of all those relationships, from initial interactions to long-term customer loyalty, can be a daunting task. That’s where Customer Relationship Management (CRM) comes in.
Definition and Core Functions of CRM
CRM, in its simplest form, is the process of organizing, managing, and analyzing customer data to build strong, lasting relationships. It’s about understanding your customers’ needs, preferences, and behaviors so you can tailor your marketing efforts to their unique interests.
Core CRM functions include:
- Centralized customer data storage: Collect and store customer information, including contact details, purchase history, past interactions, and preferences.
- Lead management: Track and nurture lead throughout the sales funnel, guiding them toward becoming paying customers.
- Sales pipeline management: Visualize the sales process, identify bottlenecks, and optimize conversion rates.
- Marketing automation: Automate repetitive tasks, such as email marketing and personalized communications, to save time and effort.
- Reporting and analytics: Gain insights into customer behavior, marketing performance, and sales trends to make informed decisions.
Key Features of CRM Systems
CRM systems come in a variety of shapes and sizes, but they all share some common features that make them invaluable tools for marketers:
- Contact management: Store and organize customer contact information, including names, email addresses, phone numbers, and social media profiles.
- Opportunity tracking: Track potential sales opportunities, including lead sources, activities, and progress toward conversion.
- Campaign management: Plan, execute, and track the performance of marketing campaigns across multiple channels.
- Customer segmentation: Divide your customer base into segments based on shared characteristics, such as demographics, interests, or purchase behavior.
- Personalized communication: Send targeted emails, offers, and marketing messages based on customer preferences.
Benefits of Implementing CRM
The benefits of implementing CRM for marketing are numerous:
- Improved customer satisfaction: By understanding your customers better, you can provide more personalized and relevant experiences, leading to increased satisfaction and loyalty.
- Increased sales productivity: CRM tools help you streamline sales processes, identify high-value leads, and close more deals faster.
- Enhanced marketing ROI: By measuring the performance of your marketing campaigns, you can optimize your spending and get better results.
- Data-driven decision-making: CRM provides a wealth of customer data that can be used to inform strategic marketing decisions.
- Improved team collaboration: CRM breaks down silos between sales and marketing, fostering collaboration and better customer outcomes.
Real-world Examples of CRM Usage
Here are some real-world examples of how companies are using CRM to transform their marketing efforts:
- E-commerce: A fashion retailer uses CRM to track customer browsing behavior, recommend personalized products, and send targeted email campaigns.
- B2B SaaS: A software company uses CRM to nurture leads through the sales process, provide personalized onboarding experiences, and track customer satisfaction.
- Hospitality: A hotel chain uses CRM to manage guest interactions, track preferences, and provide personalized recommendations for dining, spa services, and local attractions.
CRM is an essential tool for any marketing team that wants to build stronger customer relationships, improve marketing ROI, and drive business growth. By centralizing customer data, automating tasks, and providing data-driven insights, CRM empowers marketers to focus on what they do best: creating campaigns that resonate with customers and drive conversions.
Unpacking CMS (Content Management System) in Customer Management
In the world of marketing, where content is king, Content Management Systems (CMS) reign supreme. These versatile tools empower businesses to create, manage, and publish content across various platforms, from websites and blogs to mobile apps and social media.
But CMS’s reach extends beyond mere content creation; it also plays a crucial role in customer management, helping businesses connect with their audience, nurture relationships, and drive conversions.
Definition and Primary Functions of CMS
At its core, a CMS is a software platform that facilitates the creation, storage, and organization of digital content. It’s like having a virtual newsroom or publishing house at your fingertips, allowing you to effortlessly manage your content without the need for coding expertise.
Primary Functions of CMS:
- Content creation: CMS platforms provide drag-and-drop interfaces, pre-designed templates, and intuitive tools that make content creation a breeze.
- Content organization: CMSs offer efficient ways to organize and manage content, allowing you to categorize, tag, and archive content for easy retrieval.
- Content publishing: CMSs simplify the process of publishing content across various platforms, ensuring consistent branding and messaging.
- Version control: CMSs maintain a history of content changes, enabling you to revert to previous versions if needed.
- Collaboration: CMSs facilitate collaboration among team members, allowing multiple users to edit and manage content simultaneously.
Key Features of CMS Platforms
Beyond these core functions, modern CMS platforms offer a wealth of features that enhance their utility for customer management:
- SEO optimization: CMSs provide tools to optimize website content for search engines, improving visibility and organic traffic.
- Analytics: CMSs track user engagement and content performance, providing valuable insights into customer behavior.
- Mobile responsiveness: CMSs ensure that content adapts seamlessly to different devices, including smartphones and tablets.
- E-commerce integration: CMSs can be integrated with e-commerce platforms to create a unified shopping experience.
- Multilingual capabilities: CMSs support multiple languages, enabling businesses to reach a global audience.
Benefits of Using CMS in Customer Management
By embracing CMS, businesses can reap a multitude of benefits in their customer management efforts:
- Enhanced brand consistency: CMS ensures that all content across all platforms aligns with the brand’s visual style and messaging.
- Personalized experiences: CMS facilitates targeted content delivery based on user preferences and interests, fostering more personalized customer experiences.
- Improved customer engagement: Engaging content, such as blog posts, infographics, and videos, can capture attention, build trust, and encourage customer engagement.
- Nurturing customer relationships: CMS enables regular communication with customers through newsletters, announcements, and interactive content.
- Data-driven insights: CMS analytics provide valuable insights into customer behavior, preferences, and pain points, empowering businesses to make informed marketing decisions.
Case Studies Illustrating CMS Integration in Customer Management
CMSs have transformed the way businesses interact with their customers, and several case studies highlight their effectiveness:
- Starbucks: Starbucks’s mobile app leverages a CMS to provide personalized recommendations, order tracking, and seamless payment experiences.
- Nike: Nike’s CMS powers its website, allowing customers to browse products, read reviews, and purchase directly from the platform.
- The North Face: The North Face’s CMS drives customer engagement through engaging content, including blog posts, videos, and social media interactions.
- Lego: Lego’s CMS streamlines its online presence, allowing customers to explore its vast product catalog, create personalized builds, and engage with the Lego community.
- Ben & Jerry’s: Ben & Jerry’s CMS fosters customer loyalty through interactive content, such as online polls, contests, and virtual flavor creation tools.
CMS is not just about creating great content; it’s about creating a seamless customer experience that resonates with your audience and drives business growth.
By integrating CMS into your customer management strategy, you can nurture lasting relationships, enhance brand visibility, and achieve your marketing goals.
Key Differences Between CRM vs. CMS: A Tale of Two Tools
In the world of marketing, two technologies stand out as essential pillars of customer-centricity: CRM (Customer Relationship Management) and CMS (Content Management System). While both tools play crucial roles in building strong customer relationships, they differ significantly in their focus, objectives, and usage.
Data Focus vs. Content Focus
The fundamental distinction between CRM and CMS lies in their core focus. CRM is all about data, the lifeblood of customer relationships. It’s the repository where you store, organize, and analyze customer information, from contact details to purchase history, preferences, and interactions.
On the other hand, CMS is all about content, the heart of engaging customers. It’s your digital publishing tool, where you create, manage, and publish content across various channels, from websites and blogs to social media and mobile apps.
Objectives and Goals
CRM’s primary objective is to understand and manage customer data to build stronger relationships and drive business growth. It aims to:
- Centralize customer data: Collect, store, and organize customer information to provide a single, unified view of each customer.
- Nurture leads: Track and nurture leads through the sales funnel, guiding them toward becoming paying customers.
- Improve customer support: Provide efficient and personalized customer support by centralizing support requests, tracking interactions, and ensuring timely responses.
- Personalize marketing: Target marketing campaigns based on customer preferences and behaviors, enhancing engagement and ROI.
CMS’s primary objective is to create, manage, and publish engaging content that connects with customers and drives conversions. It aims to:
- Create and manage content: Provide an easy-to-use platform for creating, editing, and publishing content without coding expertise.
- Optimize content for search: Optimize website content for search engines to improve visibility and organic traffic.
- Track user engagement: Analyze user behavior and content performance to gain insights into customer engagement and preferences.
- Deliver personalized content: Target content delivery based on user interests and preferences, enhancing engagement.
User Roles and Permissions
CRM typically has a wider range of user roles and permissions, catering to various departments, including sales, marketing, customer service, and analytics. Each role has access to specific data and functionalities, ensuring data security and compliance.
CMS, on the other hand, typically has a more focused set of user roles, such as content creators, editors, and administrators. These roles are designed for managing and publishing content, ensuring consistent brand messaging and quality control.
Use Cases and Industries
CRM finds its home in businesses that prioritize customer relationships and sales conversions. It’s widely used by B2B companies, e-commerce businesses, and service providers.
CMS is ubiquitous across various industries, from retail and hospitality to technology and education. It’s particularly useful for businesses that rely on digital content to engage and acquire customers.
A Diagram to Highlight Differences
To visualize the key differences between CRM and CMS, consider these diagrams:
CRM:
Customer data → Centralized repository → Insights and analysis → Improved customer relationships and business growth
CMS:
Content creation → Content management → Content publishing → Engagement and conversionsCRM and CMS are complementary tools that work together to enhance customer experience and drive business growth. CRM manages the data that powers targeted marketing campaigns, while CMS delivers engaging content that resonates with customers. By leveraging both tools effectively, businesses can create a seamless customer journey, foster lasting relationships, and achieve their marketing goals.
V. CRM and CMS Integration: Bridging the Gap
A. The need for integration
B. Benefits of combining CRM and CMS
C. Challenges and considerations in integration
D. Successful integration of case studies
CRM and CMS Integration: Bridging the Gap
In today’s digital landscape, businesses are constantly striving to provide a seamless and personalized customer experience. This requires a strategic approach that combines customer relationship management (CRM) and content management system (CMS) technologies.
The Need for Integration
Traditionally, CRM and CMS have operated in silos, with CRM managing customer data and CMS handling content creation and publishing. While each tool has its strengths, this separation can lead to fragmented customer experiences and missed opportunities.
Benefits of Combining CRM and CMS
Integration between CRM and CMS breaks down these silos and creates a unified customer experience platform. This synergy unlocks a range of benefits:
- Personalized Customer Experiences: CRM data, such as customer preferences and purchase history, can be used to personalize content delivered through the CMS. For instance, a website can recommend products based on a user’s past purchases.
- Enhanced Lead Nurturing: CRM data can be used to track lead interactions and identify high-value prospects. The CMS can then deliver targeted content to nurture these leads through the sales funnel.
- Improved Customer Support: CRM data can be used to provide faster and more personalized customer support. Agents can access customer information directly from the CMS, enabling them to resolve issues more effectively.
- Data-Driven Marketing: CRM and CMS data can be combined to gain valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences. These insights can be used to optimize marketing campaigns and improve ROI.
Challenges and Considerations in Integration
While integration offers significant benefits, it also presents challenges:
- Data Standardization: Data formats and structures between CRM and CMS may differ, requiring standardization to ensure seamless data exchange.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating different software platforms can be complex, requiring technical expertise and careful planning.
- Security and Compliance: Data security and compliance are paramount, and integration must adhere to relevant regulations.
Successful Integration: Case Studies
Companies are successfully integrating CRM and CMS to enhance customer experiences and drive business growth. Here are a few examples:
- Adobe Experience Cloud: Adobe’s unified platform integrates CRM, CMS, and other marketing tools, providing a single view of the customer and enabling personalized experiences across all touchpoints.
- HubSpot CRM: HubSpot’s all-in-one platform combines CRM, CMS, marketing automation, and sales tools, simplifying customer management and marketing efforts.
- Magento Commerce: Magento’s e-commerce platform integrates CRM and CMS, allowing merchants to personalize product recommendations, marketing campaigns, and customer support based on customer data.
Integrating CRM and CMS is not a one-size-fits-all solution; the approach will vary depending on a company’s specific needs and infrastructure. However, for businesses aiming to create a unified customer experience and drive growth, integration is a worthwhile investment.
CSM (Customer Success Management) vs. CRM
Customer Success Management (CSM) is a modern, holistic sales philosophy and a part of a professional customer experience management strategy. It represents the evolution in complex sales that drives growth by focusing on creating and maintaining long-term, profitable relationships with customers. CSM is increasingly recognized as crucial in the success of businesses, particularly in the context of recurring revenue models.
CSM is part of a larger tradition in customer management, evolving from Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and Customer Engagement, with a focus on supporting the customer as the primary actor rather than the seller acting upon the customer .
How CSM and CRM can complement each other?
A strategic approach to CRM, encompassing customer-focused capabilities such as brand management and CRM itself, enhances the firm’s capacity to achieve success. The complementarity between CRM and other marketing capabilities, including CSM, can be more effective than deploying each capability in isolation. This synergy helps firms transform market knowledge into effective responsive actions, driving new product performance and customer value .
Also, Successful CRM implementation requires alignment with a firm’s broader marketing strategy and intra- and inter-organizational cooperation, which are also fundamental for effective CSM. A cross-functional, process-oriented approach is necessary for both CRM and CSM, positioning them at a strategic level to enhance customer value and shareholder value .
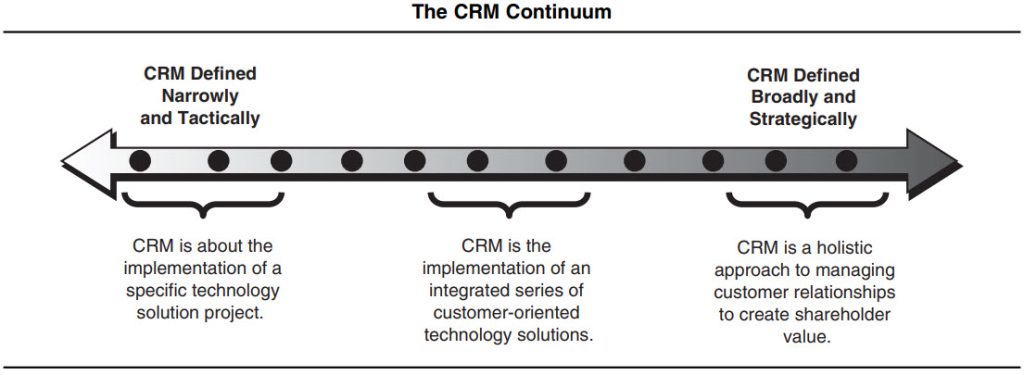
Examples of companies effectively using CSM and CRM together.
- Salesforce: As a leader in CRM software, Salesforce effectively uses its own tools to manage customer relationships. Alongside, they have developed a robust CSM approach to ensure customer success and satisfaction, focusing on helping customers maximize the use of their CRM products.
- Adobe: Known for its creative software suite, Adobe has shifted to a subscription-based model, necessitating a stronger focus on customer success to ensure ongoing subscription renewals. Their integration of CRM and CSM strategies helps maintain customer loyalty and satisfaction.
In the Future . . .
CMS vs. CRM: Contact Management Systems
- Contact management in CMS
- Contact management in CRM
- Comparative analysis of contact management features
- Best practices for contact management
The Evolving Landscape of Customer Management
- Emerging trends in CRM
- Advancements in CMS for customer management
- How AI and Automation are transforming customer management
Sources:







Responses